A computer needs the following information to function properly on a computer network:
- IP address
- Subnet Mask
- IP address of a Default Gateway (router)
- IP address of a DNS server
There are two ways that a computer can obtain those details. Either automatically, or via manual configuration.
DHCP – automatic assignment of IP addresses
In a home network, the router usually decides how the LAN should work. The router will forward traffic between the clients on the LAN and also between the LAN and the Internet.
With that in mind, it is only natural that the router also hands out IP addresses and other necessary information to the computers on the network. This is done via DHCP, which stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. In other words, it is a protocol to automatically hand out configuration to computers and other devices on the network.
Usually when you receive your home router it is already pre-configured with a DHCP server to hand out configuration to your computers and other devices. The router is also prepared so that the addresses that the router hands out via DHCP is on the same IP network as the router’s LAN IP address. This is necessary for the clients to be able to use the router as their Default Gateway.
When a computer connects to a network it will try to ask for an IP address. This is done by sending out a DHCP request where it asks if there are any available DHCP servers on the network. If any DHCP server responds then the computer will use DHCP to ask for an IP address and all the other necessary information it needs from the DHCP server.
So when your router sees this DHCP request it will hand out an available IP address from its pool of free IP addresses, together with the other details that the computer needs.
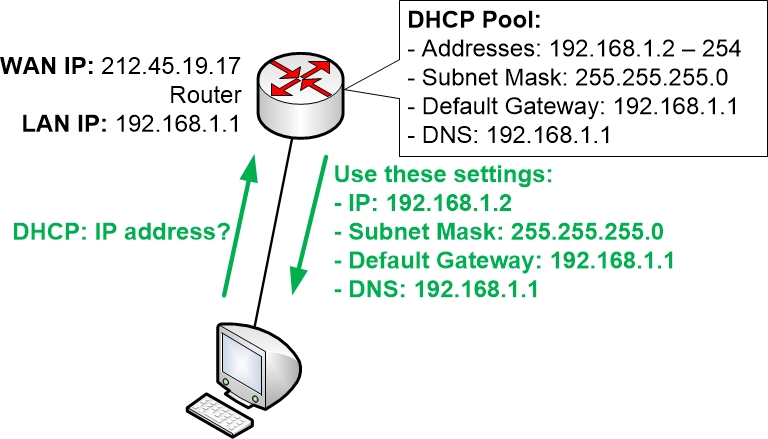
In the above example, the router’s DHCP server has a pool of available IP addresses starting with 192.168.1.2 and going all the way up to 192.168.1.254. The router will hand out the first available IP address from that pool and will mark the address as “leased” so that it does not hand out the same IP address to any other client on the network.
All clients on the LAN will receive the same Subnet Mask, Default Gateway and DNS Server settings from the DHCP server since those details are common to all clients.
Manual configuration of an IP address
Instead of letting the computer obtain its IP address from the router via DHCP you can choose to manually configure the IP settings on the computer. Normally this is avoided since it can cause a few different problems unless it is handled properly by the administrator, which is you.
When and why would you need to manually configure an IP address on a client?
If a computer obtains its IP address automatically via DHCP then it is not certain that the computer will obtain the same IP address each and every time you start the computer. The DHCP server remembers which computer that has gotten which IP address, but only for a certain amount of time. If a computer is powered off for too long (often a day or two, depending on how the router is configured) then the DHCP server will forget which IP address that it handed out to the computer. Also, if the router is powered off for any reason then it will typically forget about any DHCP leases it has previously handed out.
In some special cases, this could lead to problems. One such example is if you have had to make a Port Forward (a subject which is discussed in further details in other parts of this guide). Port forwards often point to an internal LAN IP address of a computer. As long as the computer keeps the same IP address the Port Forward will work. But if the computer changes IP addresses every so often, then after each IP address change the Port Forward must be updated in the router configuration.
In that situation, it is often recommended to configure the computer that should receive the Port Forward manually with an IP address. That way the IP address will always stay the same and the Port Forward keeps working.
When you configure an IP address manually on a computer you need to configure the same settings that a computer normally receives via DHCP:
- An available IP address on the same IP network as the router
- The same Subnet Mask that the router is using
- Default Gateway, which should be set to the LAN IP address of the router
- DNS Server address – either the router LAN IP address or another DNS server on the Internet. You may use the same address that the router normally hands out via DHCP
IP address conflicts
If you choose to manually configure an IP address on a computer, then you also should make sure to exclude that IP address from the pool of DHCP addresses in your home router. Otherwise the router might hand out the same IP address to some other computer on the network.
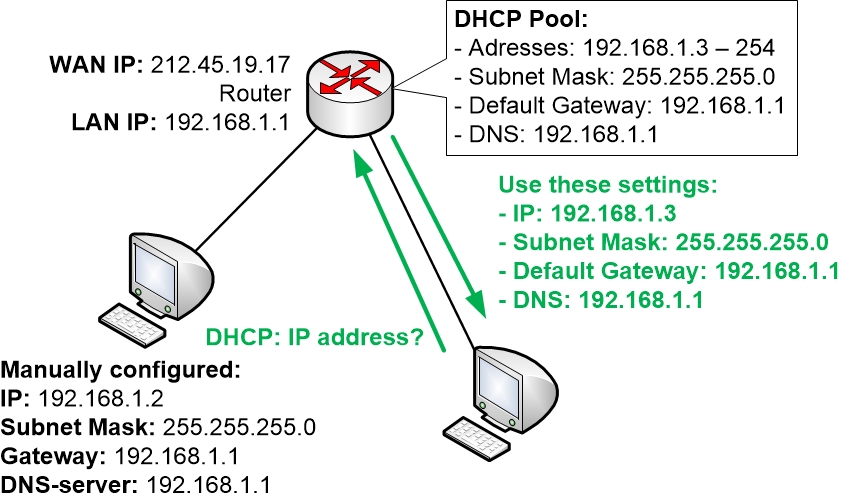
Using the street address analogy again, if two houses on the same street for some reason had the exact same house number, then the confusion would be great. Some packages and letters would end up at the correct house whereas others would end up at the wrong place. It would very much be hit and miss with a big random element to it.
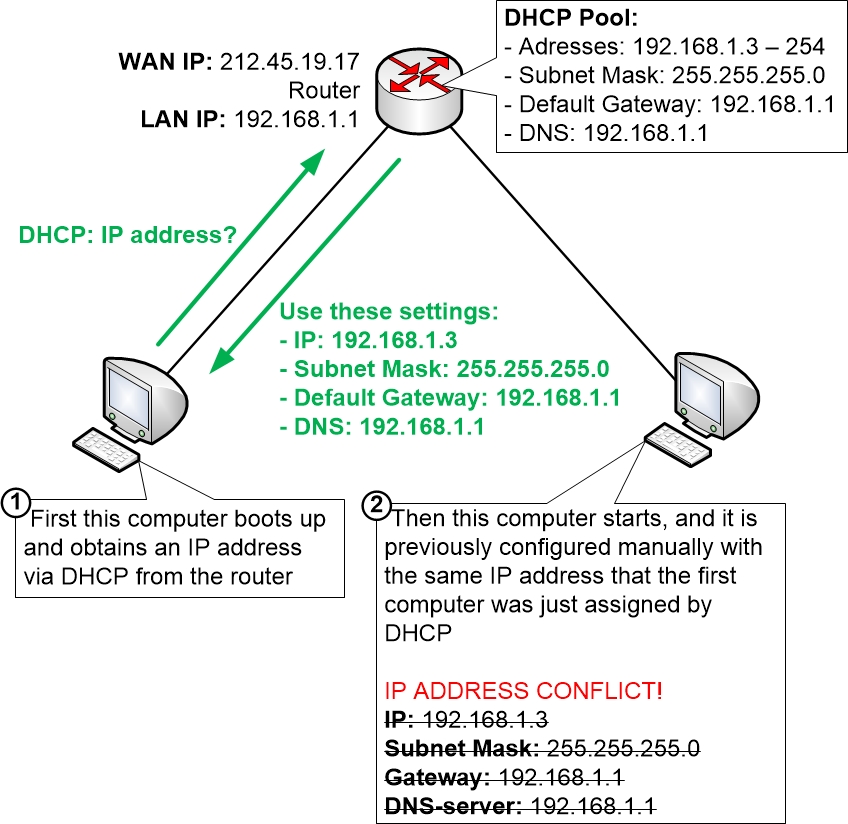
The same thing would happen on a computer network where two devices were configured to use the exact same IP address. You then have an IP address conflict on the network, and the result is basically that communication stops working for the involved clients. Network communication simply does not work if only approximately half of the traffic ends up in at the correct place.
In modern networks and with newer operating systems the computers will try to avoid IP address conflicts by checking first if the IP address seems to be taken already. But even then only the first computer that obtains the IP address will work correctly. The second computer that accidentally is given the same IP address as the first one will notice the IP address conflict and will then simply avoid talking on the network until it has been given another IP address.
|
Previous part: |
Next part: |
